ESTJ
What makes an ESTJ tick?
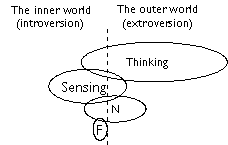
The Dominant function is the judging one of Thinking. Characteristics
associated
with this function include:
- Likes making decisions on the basis of logic, using objective
considerations
- Is concerned with truth, principles and justice
- Is analytical and critical, tending to see the flaws in situations
- Takes an objective approach
The judging Thinking function is extroverted. That is, Thinking is used
primarily to govern the outer world of actions and spoken words. The ESTJ will
therefore:
- organize life in on a logical basis, classifying, ordering, and
directing facts and situations
- be decisive, with the aim of being just and fair
- spontaneously criticize
- be comfortable with conflict as a way of resolving problems
- take an impersonal approach, focusing more on systems and organizational
needs than each individuals' feelings
The Thinking function is primarily supported by introverted Sensing
perception. That is, Sensing perception is used primarily to manage the inner
world of thoughts and emotions. This will modify the way that the Thinking is
directed, by:
- focusing the (outer world) Thinking on practical decisions that lead to
tried and trusted ways of organizing or solving problems
- focusing decisions on immediate considerations - e.g.: short term costs
and benefits, and the next step
The classic temperament of an ESTJ is Epimethean, or Melancholic, for whom a
basic driving force is duty, service and belonging.
Contributions to the team of an ESTJ
In a team environment, the ESTJ can contribute by:
- working hard and efficiently to complete tasks by the deadlines set
- contributing practical organizational skills
- applying relevant and realistic logical arguments
- calling a spade a spade
- ensuring the team follows through to completion
The potential ways in which an ESTJ can irritate others include:
- focusing too much on the current task at the expense of broader
interpersonal issues
- being too blunt in giving criticism
- not seeing the wood for the trees
- not encouraging others to experiment or innovate
- not paying enough attention to others' feelings and values
Personal Growth
As with all types, the ESTJ can achieve personal growth by developing all
functions that are not fully developed, through actions such as:
- pausing and thinking, and recognizing that others will accept the ESTJ's
direction if their own contributions are accepted and valued
- working within other people's limitations
- taking time to consider the impact of the ESTJ's approach and ideas on
people's feelings
- expressing appreciation towards others
- consulting others more, to engender ownership of the solution
- learning to acknowledge and develop the ESTJ's own emotions and personal
values
- spending time alone to develop personal long-term strategies
- spending time to develop personal relationships for their own sake
Recognizing Stress
As stress increases, 'learned behavior' tends to give way to the natural
style, so the ESTJ will behave more according to type when under greater stress.
For example, in a crisis, the ESTJ might:
- take command, decide what needs to be done, and tell everyone what to do
- use tried and trusted solutions to short-term problems
- make decisions too quickly, and without considering the impact on people
- criticize others efforts and ignore their feelings
Under extreme stress, fatigue or illness, the ESTJ's shadow may appear - a
negative form of INFP. Example characteristics are:
- withdrawing and wanting to be alone
- having intense emotions, that may or may not be expressed
- being very sensitive to criticism
- attributing unrealistic negative meaning to others actions or statements
The shadow is part of the unconscious that is often visible to others, onto
whom the shadow is projected. The ESTJ may therefore readily see these faults in
others without recognizing it in him/her self.
Return to Home Page
CLICK HERE

